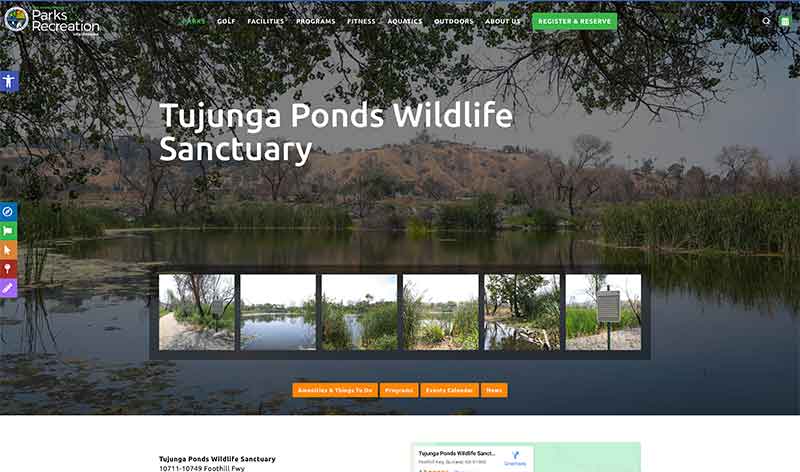
Jose Mier, promoter of all things Sun Valley, takes a look at wildlife (and domesticated animals) within and around Sun Valley, CA. Some places such as the Tujunga Ponds Wildlife Sanctuary are a great place to relax and enjoy nature as well as admiring local wildlife.
Wildlife sanctuaries play a crucial role in conserving biodiversity, offering a safe haven for animals, plants, and entire ecosystems to thrive without the threat of human interference. As populations grow and urban areas expand, these protected areas become increasingly essential for safeguarding vulnerable species from poaching, habitat loss, and other human-induced threats. By preserving natural habitats and supporting diverse ecosystems, wildlife sanctuaries not only protect individual species but also contribute to larger conservation efforts that sustain the balance of our planet’s natural systems. This article delves into the purpose of wildlife sanctuaries, their significance in conservation efforts, the variety of species they protect, and the challenges they face in today’s rapidly changing world.
The Purpose of Wildlife Sanctuaries
The primary purpose of a wildlife sanctuary is to provide a protected environment where wildlife can live in its natural habitat, free from the disruptions and dangers posed by human activities. Unlike zoos, which confine animals in artificial settings for observation, sanctuaries preserve the natural environment and allow animals to roam freely. Many sanctuaries also serve as rescue and rehabilitation centers for animals that have been injured, orphaned, or displaced due to human interference. By providing medical care and a safe space, sanctuaries help these animals recover and, when possible, reintroduce them into the wild.
Beyond simply protecting wildlife, sanctuaries often contribute to scientific research, educational initiatives, and ecotourism. Many sanctuaries partner with conservation organizations to monitor endangered species, collect data on animal behavior, and study ecosystems. This research can lead to important discoveries about animal behavior, genetics, and ecological interactions, ultimately guiding better management and conservation strategies. Additionally, educational programs offered by wildlife sanctuaries help raise awareness about environmental conservation, fostering a connection between people and the natural world.
Types of Wildlife Sanctuaries
Wildlife sanctuaries vary in type, depending on the specific species they aim to protect and the geographic location of the sanctuary. Below are a few common types:
- Bird Sanctuaries
Bird sanctuaries are dedicated to protecting bird species and their habitats. These sanctuaries often contain a range of environments such as wetlands, forests, and grasslands to support different bird species. Bird sanctuaries provide safe nesting sites and are critical for migratory birds, which rely on certain habitats at specific times of the year for resting and feeding during long migrations. - Marine Sanctuaries
Marine sanctuaries protect ocean and coastal ecosystems, covering coral reefs, kelp forests, and deep-sea habitats. These sanctuaries are vital for the conservation of marine life, including fish, coral, and larger species such as sharks, whales, and dolphins. By regulating fishing, tourism, and other activities, marine sanctuaries protect delicate marine ecosystems from overexploitation and pollution. - Forest Sanctuaries
Forest sanctuaries conserve large areas of forests, protecting not only the trees but also the diverse plant and animal species that rely on these habitats. Forest sanctuaries help mitigate climate change by maintaining forests that act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen. - Rehabilitation and Rescue Sanctuaries
Some wildlife sanctuaries specifically focus on rehabilitating animals rescued from illegal trade, poaching, or accidents. These sanctuaries provide a safe environment for recovery and offer a second chance to animals that may have otherwise perished due to human impact. While some of these animals are eventually reintroduced into the wild, others live permanently in the sanctuary if they cannot survive on their own.
The Importance of Wildlife Sanctuaries in Conservation Efforts
Wildlife sanctuaries are central to conservation efforts as they provide critical safe zones for wildlife to breed, hunt, and thrive naturally. They help preserve genetic diversity by protecting large populations of species, including endangered ones. In some cases, sanctuaries serve as breeding grounds for species that are at risk of extinction, offering a stable environment where populations can grow and eventually be reintroduced into their natural habitats.
Sanctuaries also maintain the ecological balance of their regions by supporting keystone species. These are species that have a disproportionate impact on their ecosystems and whose presence supports the survival of other species. For instance, a sanctuary that protects wolves indirectly supports the growth of vegetation and smaller species, as wolves control the population of grazing animals like deer. This interdependence among species is a key component of healthy ecosystems, and sanctuaries contribute to this balance by maintaining populations of crucial species.
Educational Value and Ecotourism
Wildlife sanctuaries are not only conservation tools but also serve as important educational platforms. Many sanctuaries offer educational programs to inform visitors about wildlife, the importance of conservation, and the threats faced by different species. These programs can include guided tours, workshops, and lectures led by conservationists or researchers. By educating the public, sanctuaries help build a more environmentally conscious society that is more likely to support conservation initiatives and policies.
Ecotourism is another significant benefit provided by wildlife sanctuaries. Unlike conventional tourism, which can be disruptive to wildlife, ecotourism is structured to minimize the impact on ecosystems and contribute directly to conservation efforts. Revenue generated from ecotourism often goes back into maintaining the sanctuary and funding conservation projects. This sustainable approach to tourism allows people to experience wildlife in their natural habitat while simultaneously supporting the sanctuary’s mission.
Challenges Facing Wildlife Sanctuaries
Despite their importance, wildlife sanctuaries face numerous challenges that threaten their ability to protect wildlife effectively:
- Habitat Loss and Encroachment
Expanding urban areas and agricultural activities are some of the biggest threats to sanctuaries, often resulting in the shrinking of natural habitats and encroachment on sanctuary boundaries. This can lead to habitat fragmentation, which isolates animal populations and reduces their chances of survival by limiting resources and breeding opportunities. - Illegal Poaching and Wildlife Trade
Poaching is a persistent problem that continues to threaten species like rhinos, elephants, and tigers, even within protected areas. Despite laws against poaching, wildlife sanctuaries often struggle with limited resources to patrol and protect their boundaries from illegal hunters and traders. - Funding and Resource Limitations
Many sanctuaries rely on government grants, donations, and ecotourism for funding. Economic downturns, natural disasters, or political instability can lead to funding shortages, which affect the sanctuary’s ability to maintain its facilities, provide medical care, and ensure the safety of the animals. - Climate Change
Climate change poses a serious threat to sanctuaries around the world, altering weather patterns and impacting food availability, breeding cycles, and migration patterns. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and shifting vegetation zones can have detrimental effects on wildlife, forcing animals to relocate or adapt quickly, which isn’t always possible. - Human-Wildlife Conflict
As human populations encroach on wildlife habitats, conflicts between people and animals have become more common. Wildlife may venture outside sanctuary boundaries in search of food or water, leading to potentially dangerous encounters with humans, as well as crop and property damage.
Prominent Wildlife Sanctuaries Around the World
Some wildlife sanctuaries have become iconic due to their success in conservation and the unique species they protect. Here are a few notable examples:
- Yellowstone National Park, USA: The first national park in the world, Yellowstone is home to a rich array of species, including bison, grizzly bears, and wolves. Its diverse ecosystem and geothermal features make it one of the most unique sanctuaries globally.
- Masai Mara National Reserve, Kenya: Known for the annual wildebeest migration, the Masai Mara is home to the “Big Five” – lions, leopards, elephants, buffalo, and rhinoceros. The reserve attracts tourists from around the world, making it a vital site for African wildlife conservation.
- Great Barrier Reef Marine Park, Australia: This marine sanctuary protects the world’s largest coral reef system, home to thousands of marine species. Climate change and coral bleaching have placed the reef in danger, making the sanctuary’s conservation efforts critical for its survival.
- Corbett National Park, India: India’s oldest national park, Corbett is known for its efforts to protect Bengal tigers. The sanctuary provides a safe haven for tigers and other species like leopards, elephants, and deer, helping maintain the balance of its ecosystem.
The Future of Wildlife Sanctuaries
As the world grapples with environmental issues such as habitat loss, climate change, and biodiversity decline, the role of wildlife sanctuaries is more important than ever. The future of sanctuaries depends on sustainable practices, global cooperation, and innovative solutions to address the growing challenges they face. Many sanctuaries are beginning to integrate technology, such as drones for monitoring poaching activity, GPS tracking for studying animal movements, and climate resilience measures to combat environmental changes.
Moreover, there is an increasing need for public support and awareness. Community involvement in conservation, through volunteer programs and local initiatives, can help protect these valuable spaces. Partnerships between governments, non-profits, and private entities are also essential for securing the funding and resources necessary for the long-term survival of wildlife sanctuaries.
Conclusion
Wildlife sanctuaries are vital to preserving the planet’s biodiversity and protecting vulnerable species. These protected areas provide safe spaces for animals to live, reproduce, and thrive in their natural habitats, all while contributing to larger conservation efforts. From forest and marine sanctuaries to bird and rehabilitation sanctuaries, each plays a unique role in maintaining ecological balance. As sanctuaries face challenges such as habitat loss, poaching, and climate change, their success will depend on continued public support, funding, and innovative conservation strategies. For future generations, wildlife sanctuaries will remain essential as they represent a collective commitment to protecting the earth’s irreplaceable natural heritage.